Différences entre versions de « MicroPython-esp32-evb »
(→GPIO) |
|||
| (19 versions intermédiaires par le même utilisateur non affichées) | |||
| Ligne 125 : | Ligne 125 : | ||
== Interface Infrarouge == | == Interface Infrarouge == | ||
| − | L'émission | + | L'émission infrarouge sur ESP32 est pris en charge par le module RMT (pour ''Remote'', voir [https://github.com/micropython/micropython/pull/5184 ce fil de discussion] sur l'implémentation de la fonctionnalité). |
| + | |||
| + | Bien que ce module soit destiné à l'émission/réception, seule l'émission semble prise en charge. | ||
[[Fichier:MicroPython-esp32-evb-IR.jpg]] | [[Fichier:MicroPython-esp32-evb-IR.jpg]] | ||
| + | === Envoyer des codes IR === | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="python"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="python"> | ||
from esp32 import RMT, Pin | from esp32 import RMT, Pin | ||
r = esp32.RMT(0, pin=Pin(12), clock_div=8, carrier_freq=38000) | r = esp32.RMT(0, pin=Pin(12), clock_div=8, carrier_freq=38000) | ||
| + | # The channel resolution is 100ns (1/(source_freq/clock_div))=1/(80 000 000/8) | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Send start->0 for 100ns, 1 for 2000ns, 0 for 200ns, 1 for 4000ns | ||
| + | r.write_pulses((1, 20, 2, 40), start=0) | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Vous pouvez éventuellement utiliser la bibliothèque '''ir_tx''' de Peter Inch (voir ci-dessous) | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Recevoir des codes IR === | ||
| + | |||
| + | Peter Inch à fait un excellent travail avec sa [https://github.com/peterhinch/micropython_ir bibliothèque '''micropython_ir'''] . | ||
| + | |||
| + | Celle-ci fonctionne parfaitement avec MicroPython sur ESP32. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Le protocole NEC est l'un des plus répandus. Si vous avez une veille télécommande, il y a de fortes changes qu'elle utilise le protocole d'émission NEC. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Fichier:MicroPython-esp32-evb-NEC-Remote.jpg|250px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Le code d'exemple suivant à été testé directement sur la plateforme ESP32-EVB (GPIO 39) | ||
| + | |||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="python"> | ||
| + | MicroPython v1.15 on 2021-04-18; ESP32 module with ESP32 | ||
| + | Type "help()" for more information. | ||
| + | >>> | ||
| + | >>> from machine import Pin | ||
| + | >>> from ir_rx.nec import NEC_8 | ||
| + | >>> | ||
| + | >>> ir = NEC_8( Pin( 39, Pin.IN), callback ) | ||
| + | >>> | ||
| + | >>> def callback( data, addr, ctrl ): | ||
| + | ... if data < 0: | ||
| + | ... print('Repeat code') | ||
| + | ... else: | ||
| + | ... print( 'Data {:02x} Addr {:04x}'.format(data,addr) ) | ||
| + | ... | ||
| + | >>> ir = NEC_8( Pin( 39, Pin.IN), callback ) | ||
| + | >>> Data 14 Addr 0000 | ||
| + | Repeat code | ||
| + | Data 0a Addr 0000 | ||
| + | Repeat code | ||
| + | Data 0a Addr 0000 | ||
| + | Repeat code | ||
| + | Repeat code | ||
| + | Repeat code | ||
| + | Repeat code | ||
| + | Repeat code | ||
| + | Repeat code | ||
| + | Data 18 Addr 0000 | ||
| + | Repeat code | ||
| + | Data 19 Addr 0000 | ||
| + | Repeat code | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | Voici les protocoles supportés par la bibliothèque micropython_ir | ||
| + | * from ir_rx.nec import NEC_8, NEC_16 | ||
| + | * from ir_rx.sony import SONY_12, SONY_15, SONY_20 | ||
| + | * from ir_rx.philips import RC5_IR, RC6_M0 | ||
| + | * from ir_rx.mce import MCE # Microsoft MCE remote control | ||
| − | + | === Ressources === | |
* [http://docs.micropython.org/en/v1.15/library/esp32.html#rmt Documentation Officielle du module RMT] | * [http://docs.micropython.org/en/v1.15/library/esp32.html#rmt Documentation Officielle du module RMT] | ||
* [http://blog.bschwind.com/2016/05/29/sending-infrared-commands-from-a-raspberry-pi-without-lirc/ Excellent article bien documenté sur la réception et décodage de signaux IR sur un GPIO]. | * [http://blog.bschwind.com/2016/05/29/sending-infrared-commands-from-a-raspberry-pi-without-lirc/ Excellent article bien documenté sur la réception et décodage de signaux IR sur un GPIO]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Interface CAN == | ||
| + | {{ambox-stop|text=Le firmware officiel ESP32 ne contient pas de classe CAN. }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | Ceci étant, nos86 à produit une [https://github.com/nos86/micropython/tree/esp32-can-driver version de MicroPython V1.13 pour ESP32 incluant un module machine_can.c] ainsi que l'exemple [https://github.com/nos86/micropython/blob/esp32-can-driver/examples/esp32_can.py esp32_can.py] autour du transciever MCP2251 (comme sur la présente carte). | ||
| + | |||
| + | Il y a bien eu une tentative de [https://github.com/micropython/micropython/pull/5310 Pull-Request #5310] mais ce dernier n'est pas arrivé à terme, il ne suivait pas l'interface {{fname|machine.CAN}} du port STM32. | ||
== Interface LAN8710A == | == Interface LAN8710A == | ||
| Ligne 149 : | Ligne 215 : | ||
lan = network.LAN( id=None, clk_type=3, mdc=Pin(23), mdio=Pin(18), power=Pin(21), phy_addr=1, phy_type=network.PHY_LAN8720 ) | lan = network.LAN( id=None, clk_type=3, mdc=Pin(23), mdio=Pin(18), power=Pin(21), phy_addr=1, phy_type=network.PHY_LAN8720 ) | ||
</nowiki> | </nowiki> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == GPIO == | ||
| + | Les GPIO disponibles sur la carte s'utilisent comme n'importe quel GPIO sous MicroPython. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Attention:''' Les fonctions de la carte (relais, CAN, IR, etc) sont également indiqué sur la documentation du GPIO | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Fichier:MicroPython-esp32-evb-GPIO.jpg]] | ||
== Où acheter == | == Où acheter == | ||
Version actuelle datée du 2 juin 2021 à 10:04
ESP32-EVB (Evaluation Board)
Olimex est une société concevant des produits de très haute qualité. Des produits conçu en vue d'une utilisation professionnelle et immunisé contre le parasitage et bruits électroniques divers. La carte d'évaluation ESP 32 ("ESP32 Evaluation Board" en anglais) n'est pas un jouet mais un produit robuste et bien conçu.
Cette carte ESP32 pour l'Internet des Objets (IoT) offre un choix de connectivités intéressant:
- WiFi,
- Ethernet filaire (100Mb ),
- Bluetooth LE,
- Connectivité CAN
- Contrôle par télécommande InfraRouge (IR).
La carte est équipée d'un circuit de recharge LiPo et d'un convertisseur DC/DC de type Step-up. La carte peut donc être alimenté par l'accu Lipo (comme un UPS) lorsque le circuit n'est plus alimenté par la fiche jack.
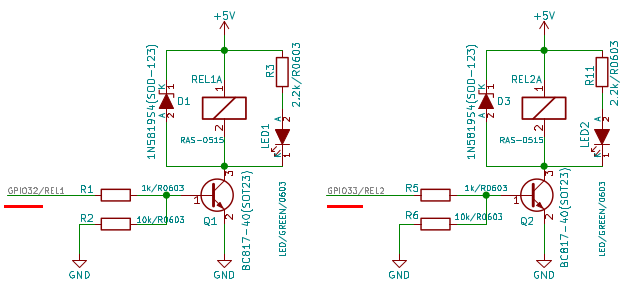
Commander les Relais
Les relais sont branchés sur les GPIO 32 et GPIO 33.
from machine import Pin
rel1 = Pin( 32, Pin.OUT )
rel2 = Pin( 33, Pin.OUT )
rel1.on()
rel1.off()
rel2.on()
rel2.off()
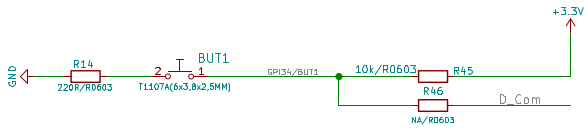
Utiliser le bouton utilisateur
Le bouton utilisateur est raccordé sur le GPIO 34.
Tel que le bouton est branché, celui-ci fonctionne en logique inversée:
- le signal sur GPIO 34 est au niveau haut (1) lorsque le bouton n'est pas pressé.
- Le GPIO 34 est au niveau bas (0) lorsque le bouton est pressé.
Cela n'étant pas naturel, la classe Signal est utilisée pour inverser le signal de la broche d'entrée (afin de revenir à une logique plus conventionnelle: 1 lorsque le bouton est pressé, 0 lorsqu'il n'est pas pressé).
from machine import Pin, Signal
from time import sleep_ms
btn_pin = Pin( 34, Pin.IN )
btn = Signal( btn_pin, invert=True )
while True:
print( btn.value() )
sleep_ms( 200 )
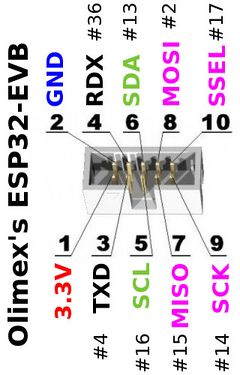
Connecteur UEXT
Le connecteur UEXT transporte une alimentation et différents bus (I2C, SPI, UARTs).
Ce connecteur est robuste et permet de brancher rapidement des cartes d'extensions UEXT (voir gamme UEXT chez Olimex, gamme UEXT chez MCHobby).
Instancier le bus I2C
from machine import I2C
i2c = I2C( sda=Pin(13), scl=Pin(16) )
Instancier le port série sur le connecteur UEXT en 9600 Bauds 8N1
from machine import UART
ser = UART(1, tx=4, rx=36, baudrate=9600 )
Instancier le bus SPI sur le connecteur UEXT se fait à l'aide de la classe SoftSPI (l'appel de SPI(-1, ....) pour définir un SPI logiciel est désuet).
# SoftSPI(baudrate=500000, *, polarity=0, phase=0, bits=8, firstbit=MSB, sck=None, mosi=None, miso=None)
# See: https://docs.micropython.org/en/latest/library/machine.SPI.html
#
from machine import SoftSPI, Pin
spi = SoftSPI( miso=Pin(15), mosi=Pin(2), sck=Pin(14), baudrate=500000 )
ssel = Pin( 17, Pin.OUT, value=1 ) # Disabled Slave Select
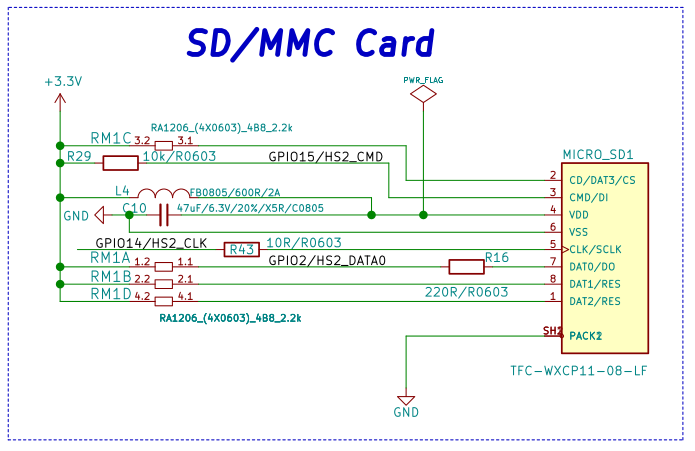
Carte SD
La carte SD utilise une seule broche de donnée --> width=1
Les slot:
- Le Slot 0 est destiné à la mémoire Flash Interne.
- Le Slot 1 correspond à sck=14, cmd=15, D0=2, D1=4, D2=12, D3=13
- Les autres slots sont décrit dans ce document.
MicroPython v1.15 on 2021-04-18; ESP32 module with ESP32
Type "help()" for more information.
>>>
>>> from machine import SDCard
>>> sdcard = SDCard( slot=1, width=1 )
>>>
>>> import os
>>> os.mount( sdcard, "/sd" )
>>> os.listdir( "/sd" )
['adafruit_feather_esp8266.md', 'adafruit_feather_esp32.md', 'adafruit_feather_rp2040.md', 'adafruit_huzzah_esp32.md', 'adafruit_huzzah_esp8266.md', 'adafruit_itsybitsy_rp2040.md', 'garatronic_pyb405.md', 'garatronic_pybstick26std.md', 'micropython_pybd_sf2w.md', 'micropython_pyboard.md', 'olimex_esp32_devkit_lipo.md', 'olimex_esp32_evb.md', 'olimex_esp8266_dev.md', 'olimex_esp8266_evb.md', 'pimoroni_pico_lipo.md', 'pimoroni_tiny_2040.md', 'raspberrypi_pico.md', 'sparkfun_micromod_rp2040.md', 'sparkfun_thing_plus_rp2040.md']
>>>
>>> # Démonter la carte SD
>>> os.umount("/sd")
>>> os.listdir( "/sd" )
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
OSError: [Errno 2] ENOENT
Ce qui correspond bien aux fichiers stockés sur la carte SD.
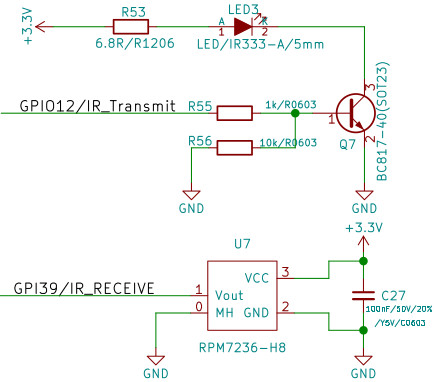
Interface Infrarouge
L'émission infrarouge sur ESP32 est pris en charge par le module RMT (pour Remote, voir ce fil de discussion sur l'implémentation de la fonctionnalité).
Bien que ce module soit destiné à l'émission/réception, seule l'émission semble prise en charge.
Envoyer des codes IR
from esp32 import RMT, Pin
r = esp32.RMT(0, pin=Pin(12), clock_div=8, carrier_freq=38000)
# The channel resolution is 100ns (1/(source_freq/clock_div))=1/(80 000 000/8)
# Send start->0 for 100ns, 1 for 2000ns, 0 for 200ns, 1 for 4000ns
r.write_pulses((1, 20, 2, 40), start=0)
Vous pouvez éventuellement utiliser la bibliothèque ir_tx de Peter Inch (voir ci-dessous)
Recevoir des codes IR
Peter Inch à fait un excellent travail avec sa bibliothèque micropython_ir .
Celle-ci fonctionne parfaitement avec MicroPython sur ESP32.
Le protocole NEC est l'un des plus répandus. Si vous avez une veille télécommande, il y a de fortes changes qu'elle utilise le protocole d'émission NEC.
Le code d'exemple suivant à été testé directement sur la plateforme ESP32-EVB (GPIO 39)
MicroPython v1.15 on 2021-04-18; ESP32 module with ESP32
Type "help()" for more information.
>>>
>>> from machine import Pin
>>> from ir_rx.nec import NEC_8
>>>
>>> ir = NEC_8( Pin( 39, Pin.IN), callback )
>>>
>>> def callback( data, addr, ctrl ):
... if data < 0:
... print('Repeat code')
... else:
... print( 'Data {:02x} Addr {:04x}'.format(data,addr) )
...
>>> ir = NEC_8( Pin( 39, Pin.IN), callback )
>>> Data 14 Addr 0000
Repeat code
Data 0a Addr 0000
Repeat code
Data 0a Addr 0000
Repeat code
Repeat code
Repeat code
Repeat code
Repeat code
Repeat code
Data 18 Addr 0000
Repeat code
Data 19 Addr 0000
Repeat code
Voici les protocoles supportés par la bibliothèque micropython_ir
- from ir_rx.nec import NEC_8, NEC_16
- from ir_rx.sony import SONY_12, SONY_15, SONY_20
- from ir_rx.philips import RC5_IR, RC6_M0
- from ir_rx.mce import MCE # Microsoft MCE remote control
Ressources
- Documentation Officielle du module RMT
- Excellent article bien documenté sur la réception et décodage de signaux IR sur un GPIO.
Interface CAN
| Le firmware officiel ESP32 ne contient pas de classe CAN. |
Ceci étant, nos86 à produit une version de MicroPython V1.13 pour ESP32 incluant un module machine_can.c ainsi que l'exemple esp32_can.py autour du transciever MCP2251 (comme sur la présente carte).
Il y a bien eu une tentative de Pull-Request #5310 mais ce dernier n'est pas arrivé à terme, il ne suivait pas l'interface machine.CAN du port STM32.
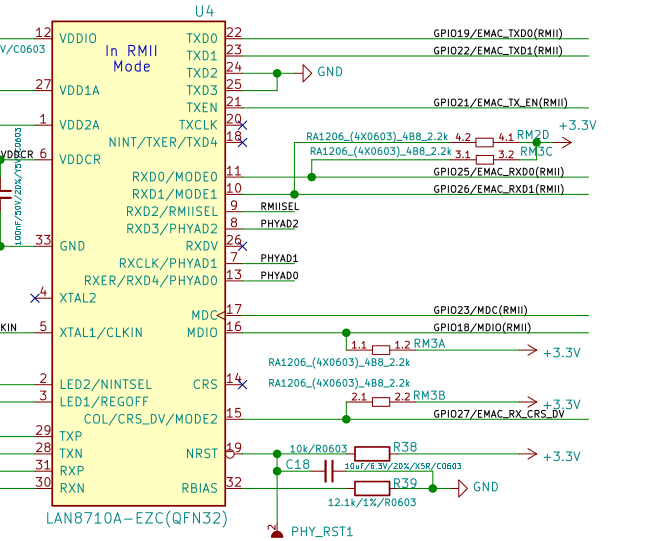
Interface LAN8710A
| Il n'y a pas de Firmware ESP32 pré-compilé contenant la classe LAN! Il faudra compiler votre propre firmware. |
D'après les informations collectées sur Lobiris.eu, il faudrait créer une instance de la classe LAN à l'aide de
# A vérifier lan = network.LAN( id=None, clk_type=3, mdc=Pin(23), mdio=Pin(18), power=Pin(21), phy_addr=1, phy_type=network.PHY_LAN8720 )
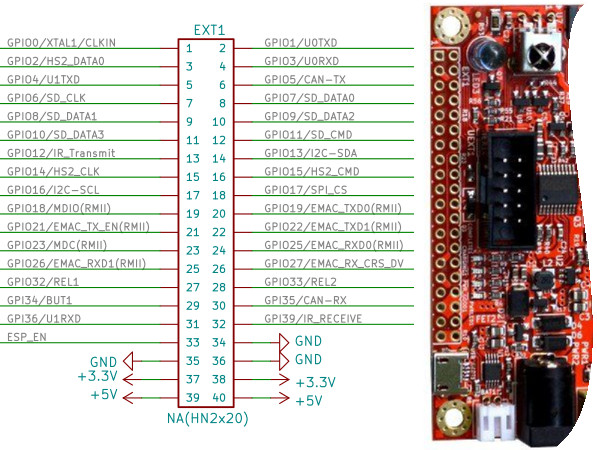
GPIO
Les GPIO disponibles sur la carte s'utilisent comme n'importe quel GPIO sous MicroPython.
Attention: Les fonctions de la carte (relais, CAN, IR, etc) sont également indiqué sur la documentation du GPIO
Où acheter
- ESP32-EVB @ MCHobby
- ESP32-EVB @ Olimex
- gamme UEXT chez Olimex
- gamme UEXT chez MCHobby