ENG-CANSAT-BMP280
Install the Library
Manual Installation
The Adafruit's BMP280 is provided with a library available on GitHub.
You can download and install the library manually by dowloading it from the BMP280 Repository.
Note that BMP280 library rely on the Adafruit_Sensor library which declare an unified data structure to store data across all the Adafruit's Sensors Libraries.
Easier Installation
You can also use the "Library Manager" to ease the installation of the BMP280 library.
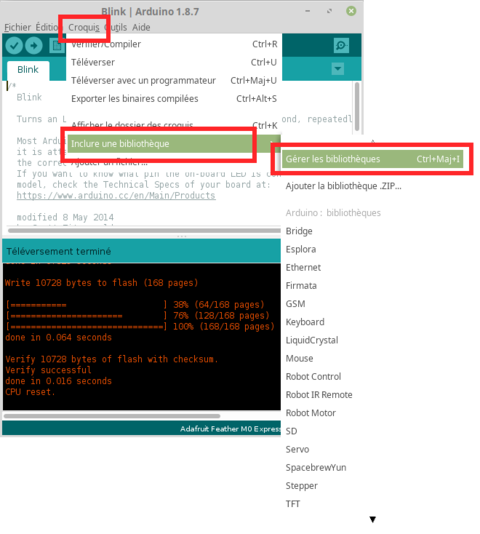
From the "Sketch" menu, select the sub-menu "Include library" --> "Library Manager" like shown on the picture here under.
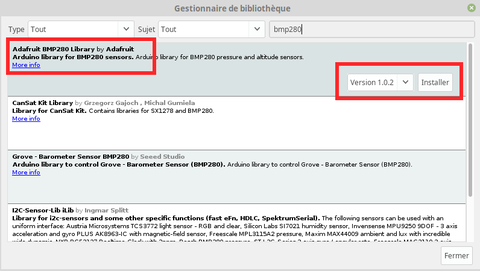
In the library manager, key-in the value "BMP280" in the search box. Then click on the install button in the front of the Adafruit BMP280 Library by Adafruit.
Great, the BMP280 library is now installed!
| You must also install the unified sensor library! If not yet done, proceed the installation of the library as described here under. |
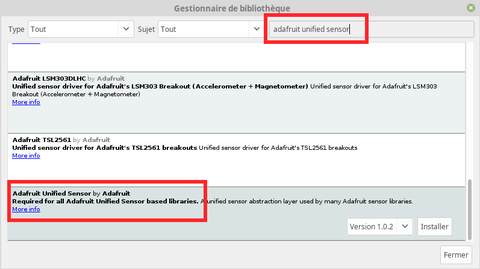
From "Library Manager", search for the "Adafruit Unified Sensor" like shown on the picture here under.
Then install it.
Wiring the sensor
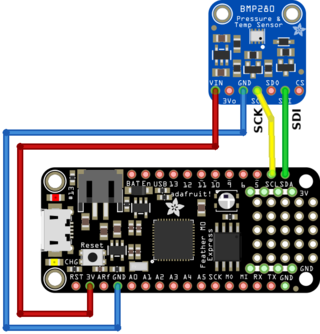
The BMP280 is wired on the I2C bus of the Feather.
Testing the sensor
The sensor can be easily tested with the Adafruit Example code (installed with the library).
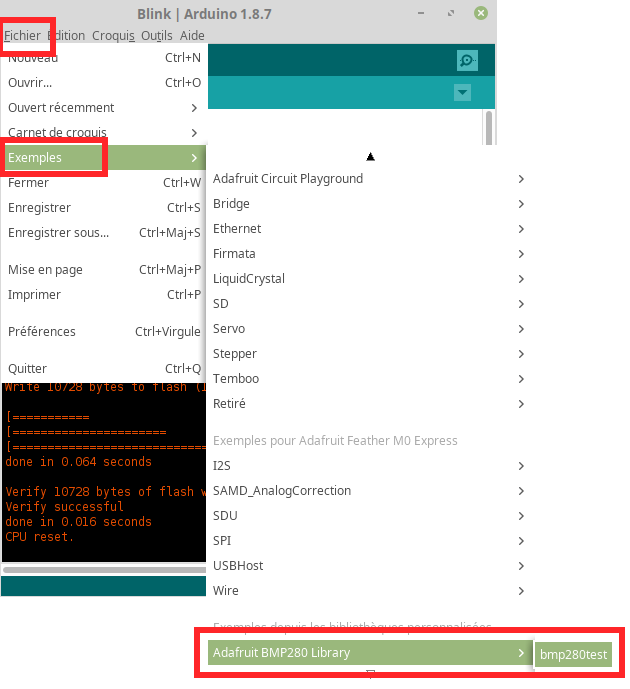
The sample code is available through the File menu under the sub-menu Example --> Adafruit BMP280 Library --> BMP280test.
The content of the example code is displayed here under (and reduced to the minimum lines for better reading).
#include <Wire.h>
#include <Adafruit_Sensor.h>
#include <Adafruit_BMP280.h>
Adafruit_BMP280 bme; // I2C
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial.println(F("BMP280 test"));
if (!bme.begin()) {
Serial.println("Could not find a valid BMP280 sensor, check wiring!");
while (1);
}
}
void loop() {
Serial.print("Temperature = ");
Serial.print(bme.readTemperature());
Serial.println(" *C");
Serial.print("Pressure = ");
Serial.print(bme.readPressure());
Serial.println(" Pa");
Serial.print("Approx altitude = ");
// 1013.25 is the pressure at sea level. It should be ajusted
// with your local forecast for a corect evaluation of altitude
Serial.print(bme.readAltitude(1013.25));
Serial.println(" m");
Serial.println();
delay(2000);
}
Compile and upload to sketch the board.
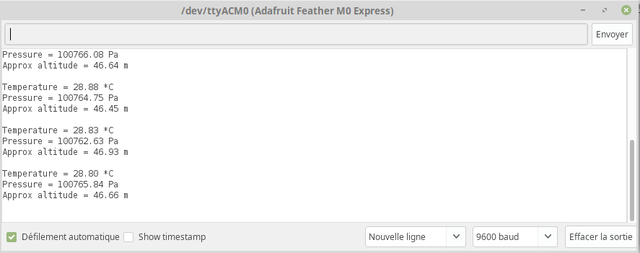
Then open the serial monitor (configured at 9600 baud) and you should see the following on the screen.
The sketch display pressure and other parameter every 2 seconds.
Pressure and altitude
About pressure reading
The pressure is returned in Pascals (an unit from International System of Units). 100 Pascals = 1 hPa = 1 millibar. The barometric pressure is often using the millibar or mm of mercury as unit. Just note that 1 pascal = 0.00750062 mm of mercury mercure.
Sea level pressure
You can also calculate the altitude from the pressure. However, to proprely measure the altitude, you need to know the pressure at the sea level (hPa, pressure that change every day)!. The BMP280 is really precise, however it may be difficult to have precise evaluation of the altitude if you don't know the pressure at the sea level (the pressure of day at the sea level).
Written by Meurisse D. from MC Hobby - License: CC-SA-BY.