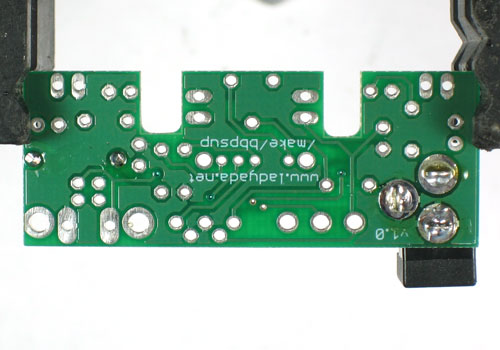
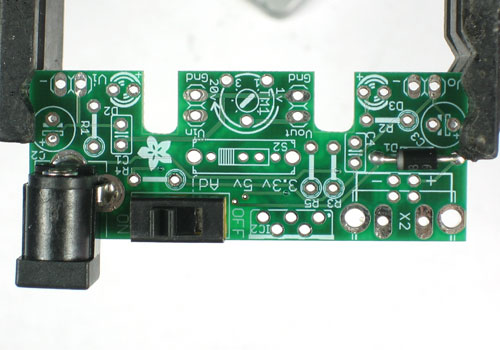
Différences entre versions de « ADF-ADJ-BBALIM-SOUDER »
| Ligne 3 : | Ligne 3 : | ||
[[Fichier:ADF-ADJ-BBALIM-SOUDER-01.jpg]] | [[Fichier:ADF-ADJ-BBALIM-SOUDER-01.jpg]] | ||
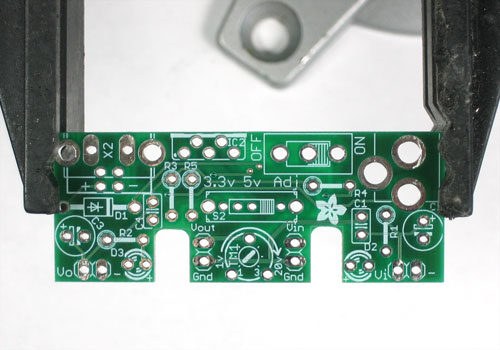
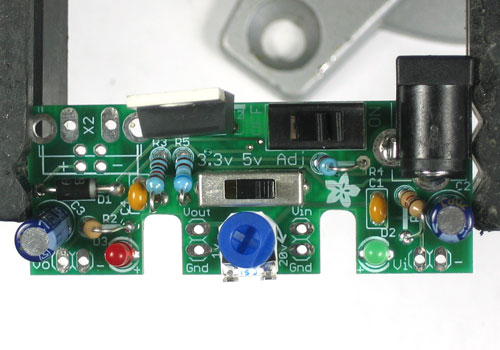
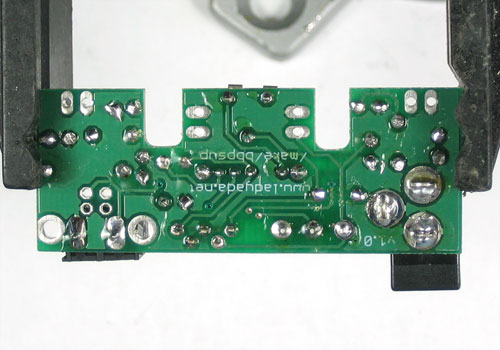
| − | + | Avant de commencer à assembler ce kit, vérifiez la liste des pièces disponibles pour vous assurer de tout avoir! | |
| − | + | Ensuite, faite chauffer votre fer à souder et nettoyez votre bureau. | |
| − | + | Placez la carte sur un [http://mchobby.be/PrestaShop/product.php?id_product=154 Panavise] afin de pouvoir travailler plus facilement. | |
[[Fichier:ADF-ADJ-BBALIM-SOUDER-02.jpg]] | [[Fichier:ADF-ADJ-BBALIM-SOUDER-02.jpg]] | ||
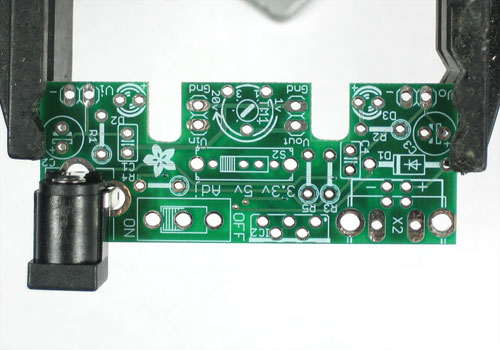
| − | + | Nous allons commencer en plaçant la prise Jack. C'est l'emplacement où sera raccorder la fiche de l'alimentation sur la carte. | |
| − | + | Cette prise Jack de 2.1mm est la taille plus répandue. | |
| + | |||
| + | La composant ne peut être utilisé que d'une seule façon, il est donc très facile de l'utiliser. | ||
[[Fichier:ADF-ADJ-BBALIM-SOUDER-03.jpg]] | [[Fichier:ADF-ADJ-BBALIM-SOUDER-03.jpg]] | ||
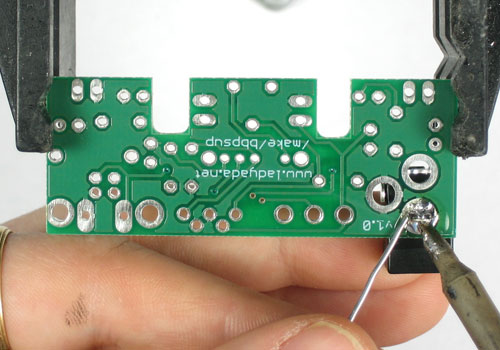
| − | + | Retournez le PCB - vous pouvez fixer le Jack à l'aide de papier collant ou en le maintenant en place avec votre doigt. | |
| − | + | Souder les 3 grosses pattes qui servent à alimenter la carte. | |
| − | + | Utilisez beaucoup de soudure! Cela assure une bonne connexion électrique et une bonne résistance mécanique... ce connecteur doit être solidement fixé. | |
[[Fichier:ADF-ADJ-BBALIM-SOUDER-04.jpg]] | [[Fichier:ADF-ADJ-BBALIM-SOUDER-04.jpg]] | ||
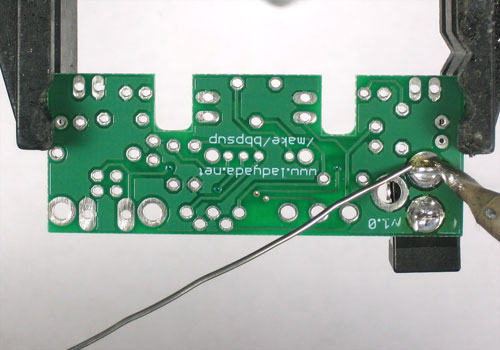
| Ligne 29 : | Ligne 31 : | ||
[[Fichier:ADF-ADJ-BBALIM-SOUDER-06.jpg]] | [[Fichier:ADF-ADJ-BBALIM-SOUDER-06.jpg]] | ||
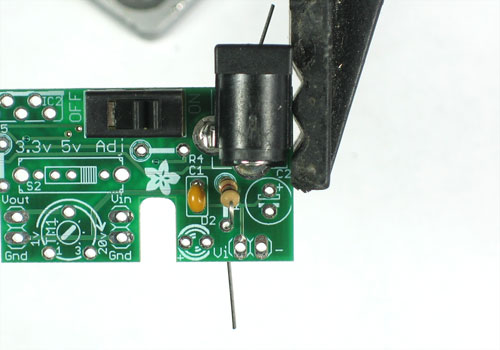
| − | + | Nous allons ensuite souder la diode de protection 1N5818. Les diodes conduisent l'électricité que dans un seul sens. | |
| + | |||
| + | Cela signifie que nous pouvons les utiliser pour protéger le circuit contre les tensions négatives - l'un des incidents les plus courants et les plus expéditifs en électronique! | ||
| + | |||
| + | Courber les pattes de la diode en forme d’agrafe comme ceci. | ||
| − | + | Notez qu'un coté porte une marque blanche/argentée. | |
[[Fichier:ADF-ADJ-BBALIM-SOUDER-07.jpg]] | [[Fichier:ADF-ADJ-BBALIM-SOUDER-07.jpg]] | ||
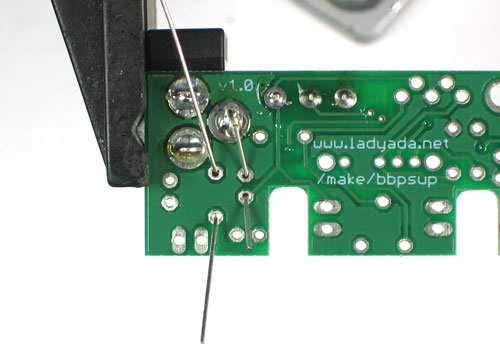
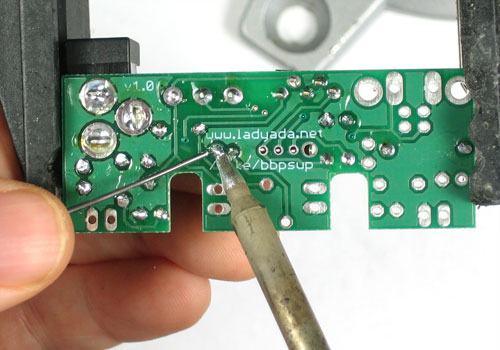
| − | + | Placez la diode sur l'emplacement marqué '''D1''' | |
| − | + | Avez-vous remarqué la marque blanche également présente sur la sérigraphie? Faite en sorte que la marque sur la diode soit au dessus de la marque présente sur la sérigraphie. Sinon le circuit ne fonctionnera absolument pas! | |
| − | + | Ajustez les pattes de la diode de sorte qu'elle soit bien à plat sur le PCB (la carte). | |
[[Fichier:ADF-ADJ-BBALIM-SOUDER-08.jpg]] | [[Fichier:ADF-ADJ-BBALIM-SOUDER-08.jpg]] | ||
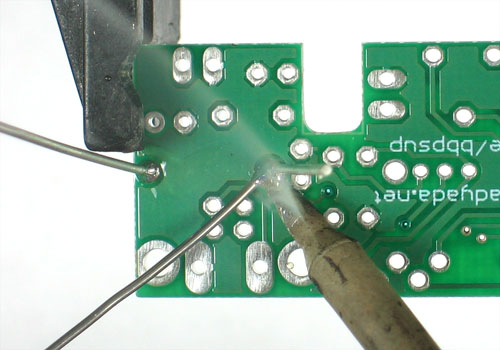
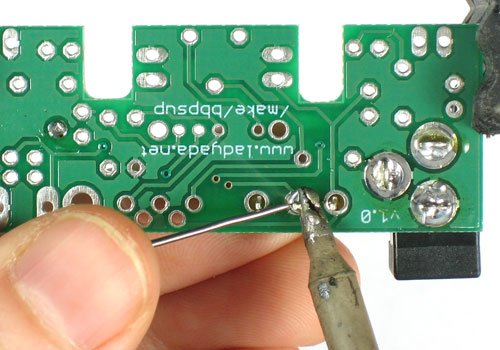
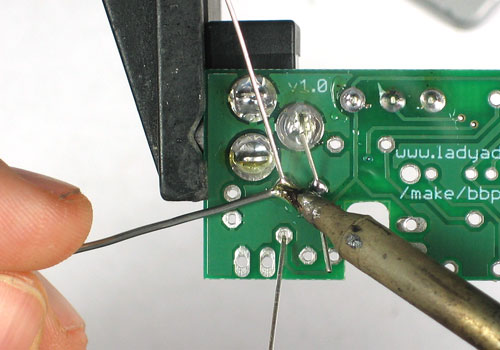
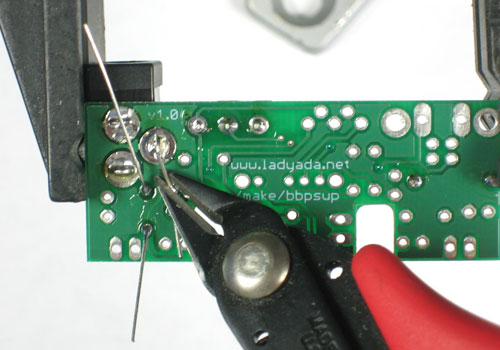
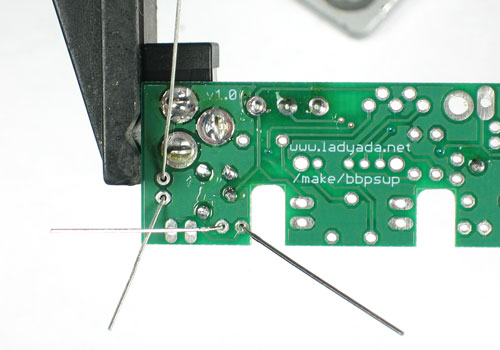
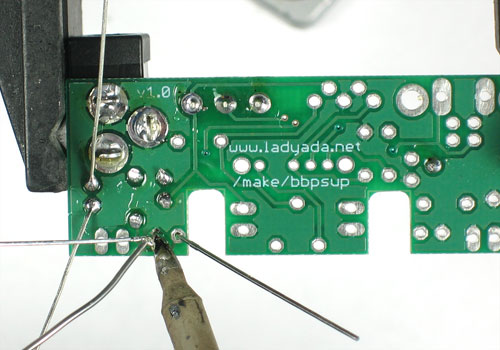
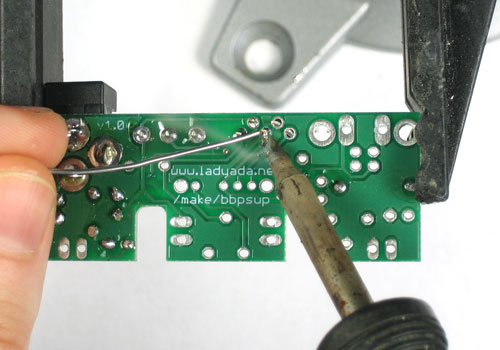
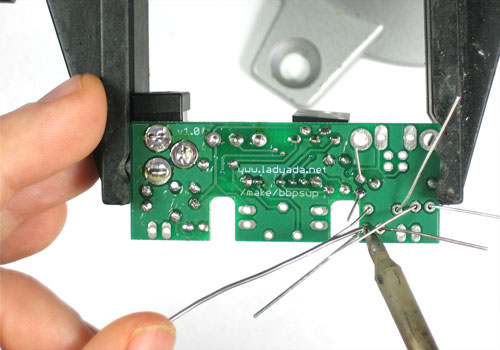
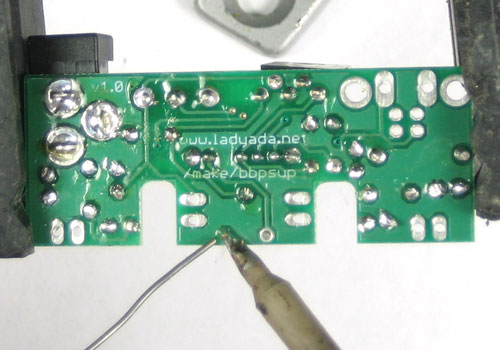
| − | + | Soudez maintenant les deux fils sur le PCB. | |
| − | + | Pour souder les pattes: placer le côté plat du fer a souder sur le fil et la pastille (l'anneau argenté sur le PCB) pendant quelques secondes et ajoutez ensuite un peu de soudure. Retirer le fil de soudure et ensuite le fer. La jointure de la soudure doit former un petit cone. | |
[[Fichier:ADF-ADJ-BBALIM-SOUDER-09.jpg]] | [[Fichier:ADF-ADJ-BBALIM-SOUDER-09.jpg]] | ||
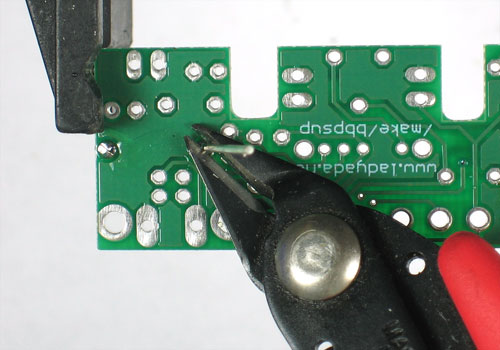
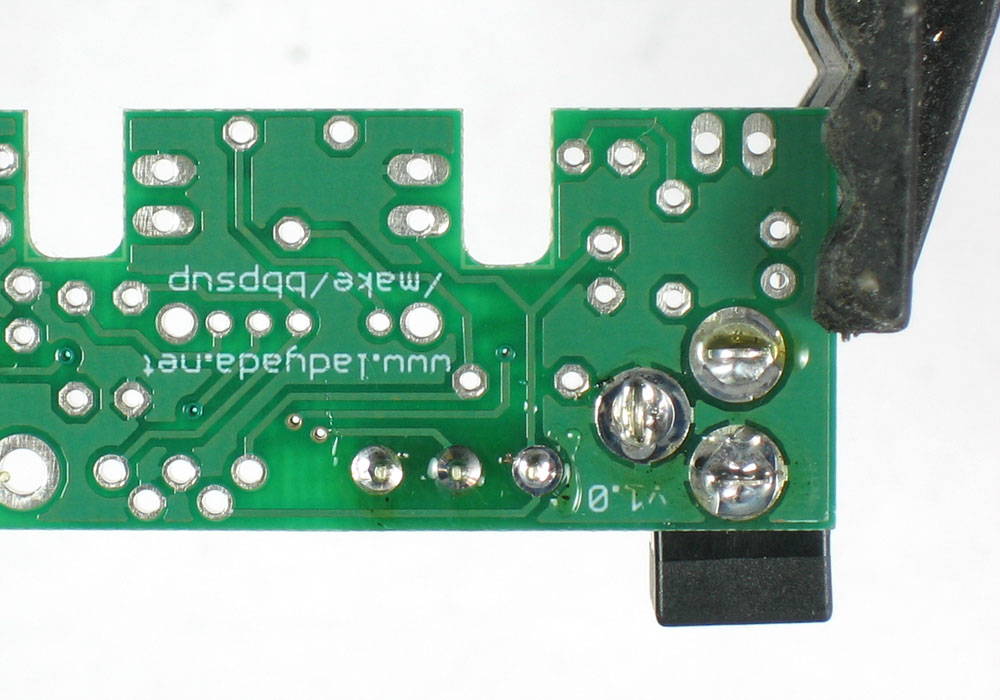
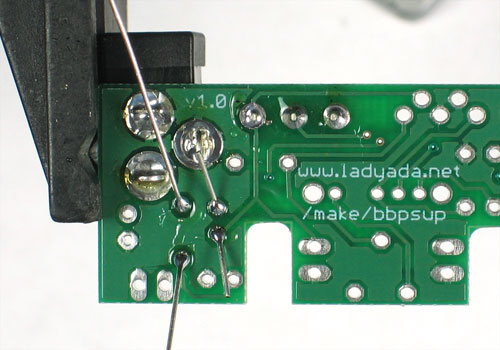
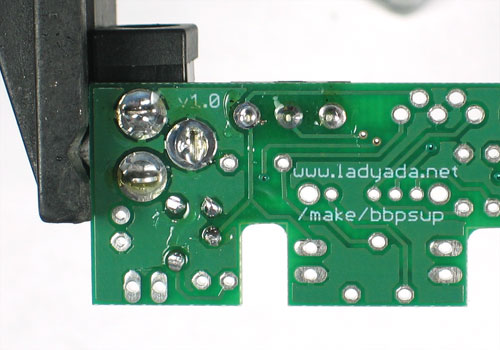
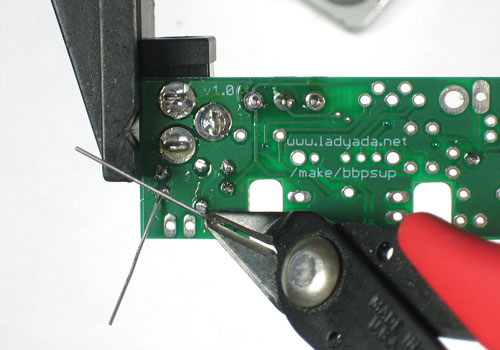
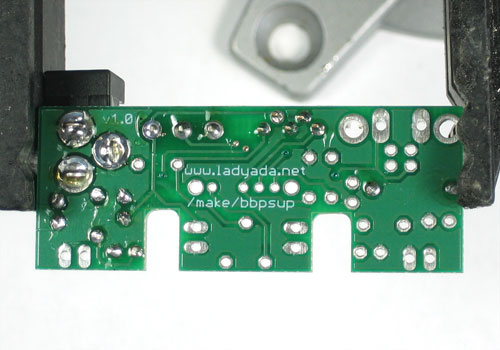
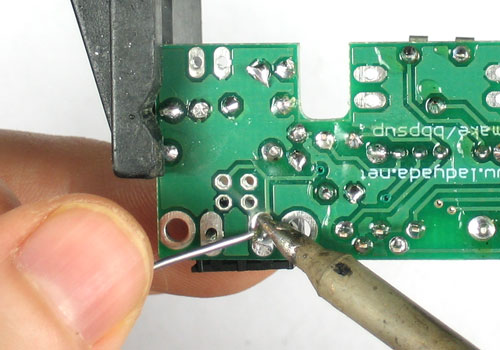
| − | + | Utilisez ensuite une pince coupante pour couper fils juste au dessus du point de soudure. | |
[[Fichier:ADF-ADJ-BBALIM-SOUDER-10.jpg]] | [[Fichier:ADF-ADJ-BBALIM-SOUDER-10.jpg]] | ||
Version du 8 novembre 2012 à 11:44
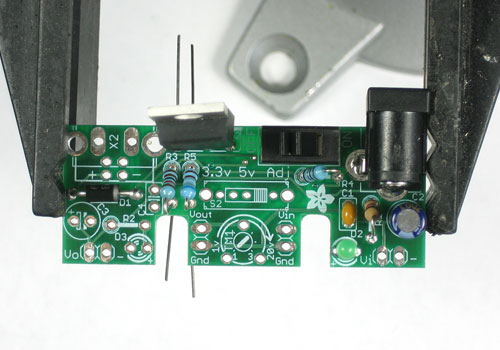
Avant de commencer à assembler ce kit, vérifiez la liste des pièces disponibles pour vous assurer de tout avoir!
Ensuite, faite chauffer votre fer à souder et nettoyez votre bureau.
Placez la carte sur un Panavise afin de pouvoir travailler plus facilement.
Nous allons commencer en plaçant la prise Jack. C'est l'emplacement où sera raccorder la fiche de l'alimentation sur la carte.
Cette prise Jack de 2.1mm est la taille plus répandue.
La composant ne peut être utilisé que d'une seule façon, il est donc très facile de l'utiliser.
Retournez le PCB - vous pouvez fixer le Jack à l'aide de papier collant ou en le maintenant en place avec votre doigt.
Souder les 3 grosses pattes qui servent à alimenter la carte.
Utilisez beaucoup de soudure! Cela assure une bonne connexion électrique et une bonne résistance mécanique... ce connecteur doit être solidement fixé.
Nous allons ensuite souder la diode de protection 1N5818. Les diodes conduisent l'électricité que dans un seul sens.
Cela signifie que nous pouvons les utiliser pour protéger le circuit contre les tensions négatives - l'un des incidents les plus courants et les plus expéditifs en électronique!
Courber les pattes de la diode en forme d’agrafe comme ceci.
Notez qu'un coté porte une marque blanche/argentée.
Placez la diode sur l'emplacement marqué D1
Avez-vous remarqué la marque blanche également présente sur la sérigraphie? Faite en sorte que la marque sur la diode soit au dessus de la marque présente sur la sérigraphie. Sinon le circuit ne fonctionnera absolument pas!
Ajustez les pattes de la diode de sorte qu'elle soit bien à plat sur le PCB (la carte).
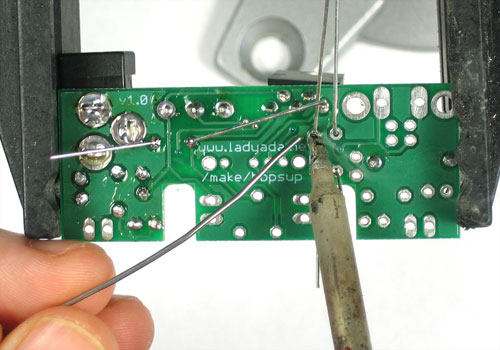
Soudez maintenant les deux fils sur le PCB.
Pour souder les pattes: placer le côté plat du fer a souder sur le fil et la pastille (l'anneau argenté sur le PCB) pendant quelques secondes et ajoutez ensuite un peu de soudure. Retirer le fil de soudure et ensuite le fer. La jointure de la soudure doit former un petit cone.
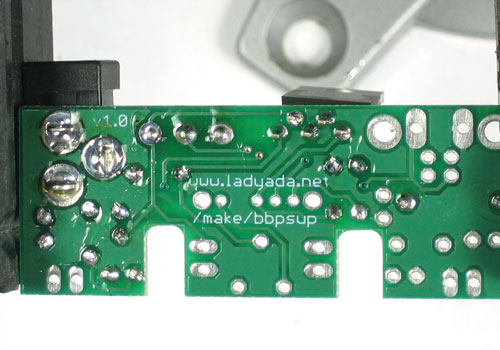
Utilisez ensuite une pince coupante pour couper fils juste au dessus du point de soudure.
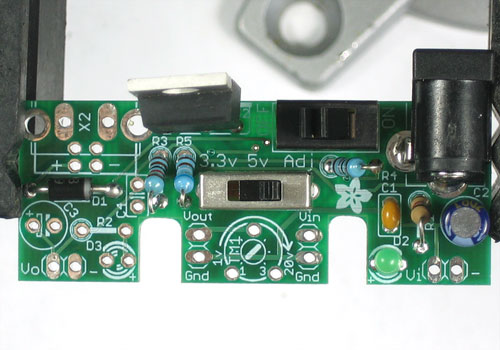
Now flip back over. Next we wil solder in the ON/OFF switch! Its pretty clear what we use it for :)
The switch is 'symmetric' so don't worry about putting it in backwards because it is the same either way.
Tape or hold the switch in place while you solder all three pins.
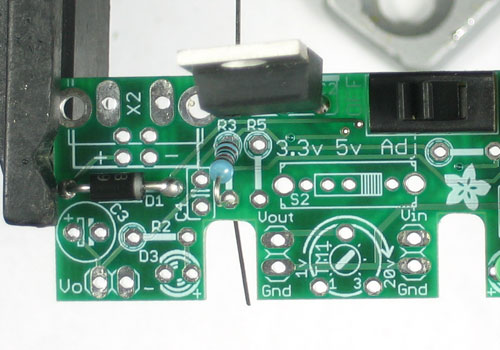
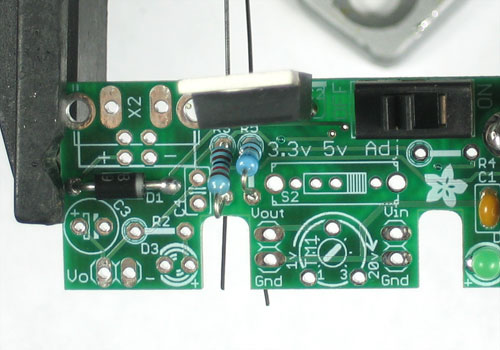
We're going to solder one of the 1.0K resistors in next. The resistors should be bent over 180 like shown. Note that resistors are 'non-polarized' so you can put them in 'either way' - they work the same forwards or backwards.
Place one of the 1.0K resistors (Brown Black Red Gold) into the slot marked R1. Then place right next to it one of the 0.1uF ceramic capacitors (they're small and yellow). The resistors and ceramic capacitors are non-polarized so they can go in 'either way'
The resistor sets the brightness of the 'high voltage' indicator LED. The 0.1uF capacitor provides high frequency filtration to make the power supply cleaner.
Bend the leads out so that the parts don't fall out when you flip over the board
Solder in the two components
Then clip the long leads off.
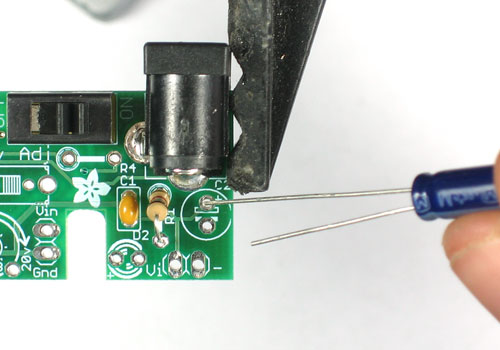
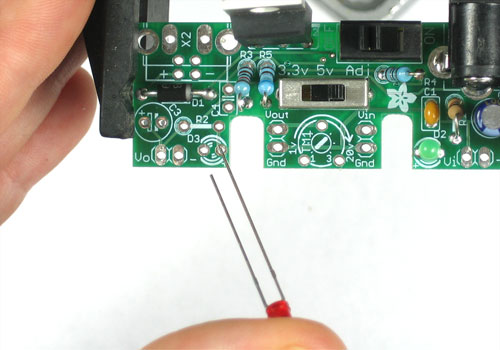
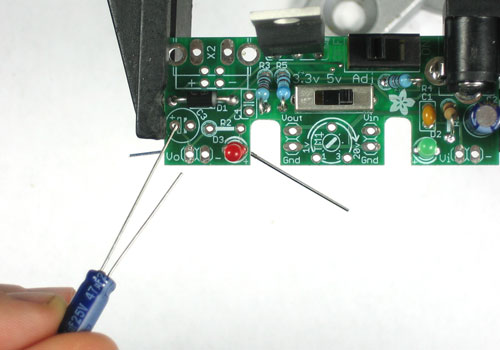
Now we will place one of the 47uF electrolytic capacitors C2
This component provides low-frequency filtration to clean up the 'high voltage' power line.
Electrolytic capacitors are polarized that means they must go in the right way or they will make your kit not work! See how one leg of the capacitor is longer? That is the positive (+) lead. Make sure that lead goes into the pad marked with a +. See the image left for details
We will finish up the 'high voltage' power supply side by placing the green indicator LED. This LED will let us know that power is working! LEDs are diodes so they are polarized. If not placed correctly they will not work! So make sure you get this right.
See how one leg of the LED is longer? That is the positive (+) lead. Make sure that lead goes into the pad marked with a +. See the image left for details
Bend the leads out so the parts sit flat against the PCB.
Solder and clip the leads.
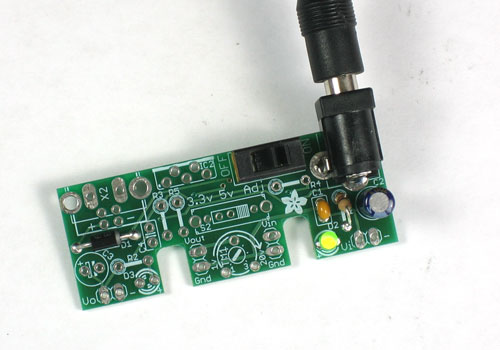
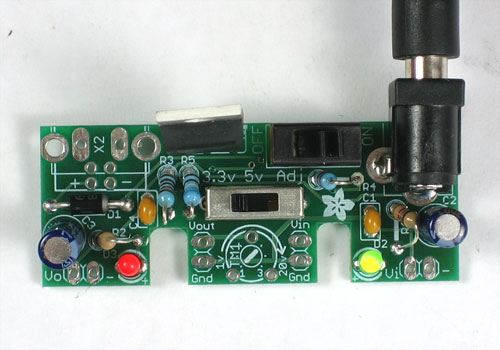
Lets take a break and test the current progress. Take the kit out of the vise and make sure there are no stray wires kicking around that could cause the board to short.
Plug in a DC power supply, center positive. Switch the power switch to the ON position. You should see the green LED light up.
If it doesnt, check that you have a center-positive power supply, that the diode is in right, etc. You may also want to test the voltage at the V- and (-) pads near the LED to see if you are seeing a voltage there.
See my multimeter tutorial for information on how to perform these tests. http://www.ladyada.net/learn/multimeter/
Once you've verified its all good, lets continue assembly.
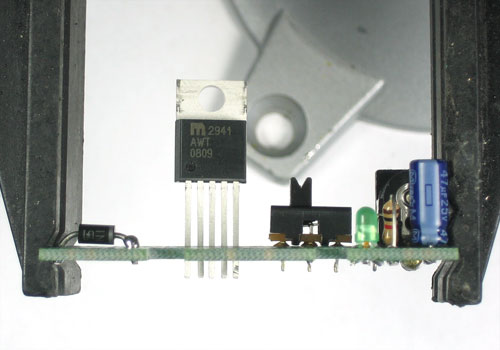
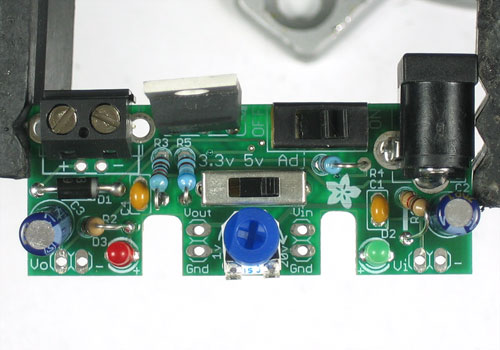
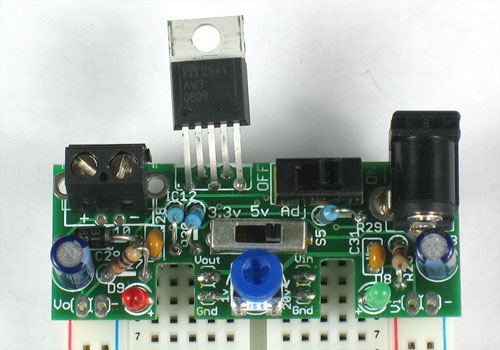
Now we will solder in the heart of the kit, the MIC2941 adjustable voltage regulator. The regulator must be placed correctly to work. Make sure that the big silver tab is at the edge of the PCB (theres a thick white line on the silkscreen to indicate it)
You'll want to solder the part so it sticks up some - that way you can attach a heatsink easily - as shown.
Solder the regulator in. If you placed the regulator as suggested, you shouldn't have to clip the leads as they'll be short.
The regulator uses resistors to set the adjustable output voltages. We'll now solder those in.
First is 11.0K R3 (Brown Brown Black Red Brown) - this resistor sets the 3.3V output level.
Second is 6.49K R5 (Blue Yellow White Brown Brown) - this resistor is the 'reference' divider for all the voltages
Third is 20.5K R4 (Red Black Green Red Brown) - this resistor sets the 5V output voltage
Solder and clip the three resistors.
Now we need a way to select which resistor is connected to the regulator. For that we use a 3-way switch. The switch can only go in one way.
Solder in all the legs of the switch.
Be careful because the solder points are small and somewhat close together. Make sure you don't have a short circuit and that each point is soldered
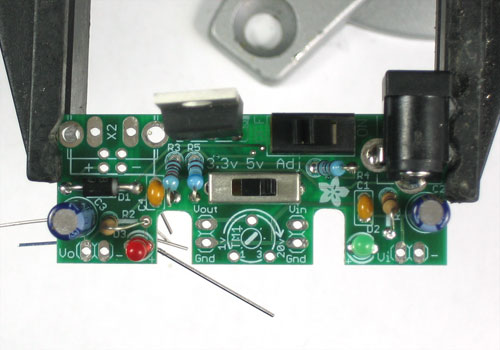
Now we will put in the capacitors and LEDs for the left hand "low voltage" side. First is the red indicator LED. Remember LEDs are polarized. Make sure the long lead goes into the (+) marked pad
Next is the large electrolytic capacitor. Just like the other one, its polarized. Make sure the long lead goes into the (+) marked pad.
Finish off the 'low voltage' side by inserting the second 1.0K resistor R2 and the second 0.1uF ceramic capacitor C4
Solder and clip all the leads
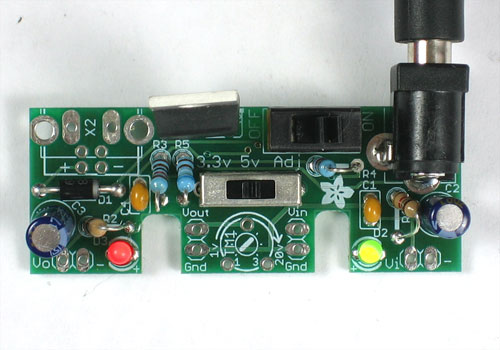
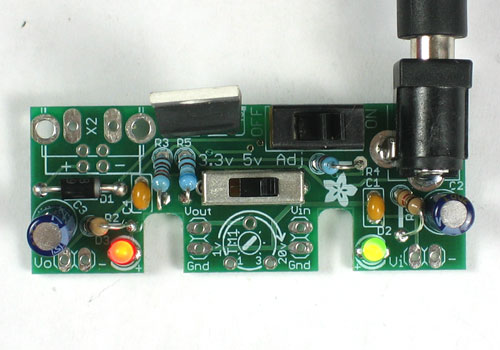
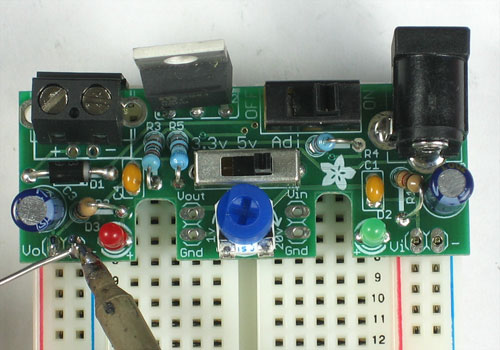
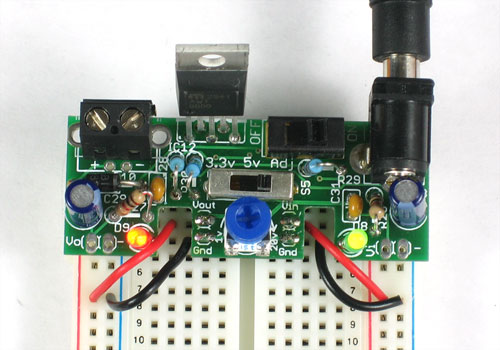
Lets take another break and quickly test what we've done so far.
Remove the PCB from the vise and clear off the tape from wire bits. Then plug in your DC power supply again
Switch the kit ON and switch the voltage selection switch from 3V to 5V to Adj. The red LED should change in brightness. It should be dim at 3V, brighter at 5V and brightest at Adj. (we haven't put in the adjusting potentiometer yet)
Lets finish up this kit!
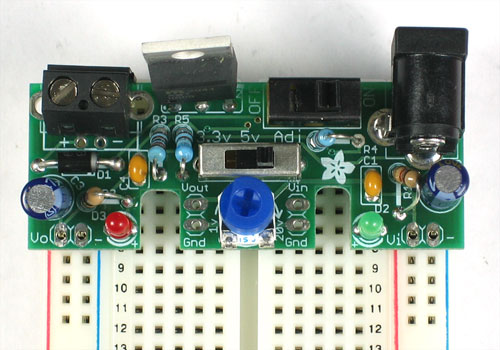
Place the 100K trim potentiometer in the middle. This is what lets us adjust the voltage output from 1.25V to 20V
The trimmer sits above the PCB a bit, this is OK.
Next we will solder in the 2-pin terminal jack. This lets us connect up wires to power the board from a battery or similar.
Make sure that the 'holes' of the terminal block are facing out so that you can plug wires in!
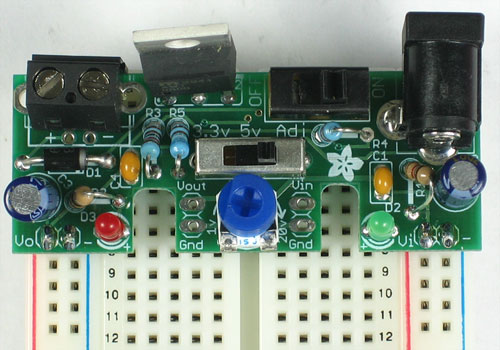
You've finished the power supply, now onto the 'breadboard' part!
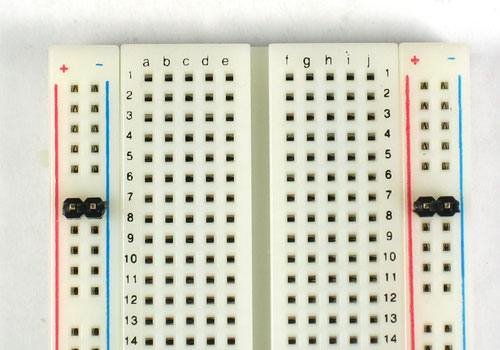
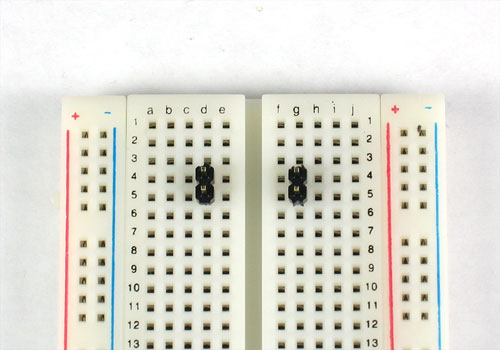
Break off 2 2-pin pieces of header and stick them into the two power rails on the side of the breadboard
Now place the power supply on top. If it fits nicely, solder the four pins.
Some breadboards are spaced differently, in which case you will have to skip ahead.
If your breadboard has nonstandard spacing, you can still plug it in using the header-breakouts in the middle.
You'll need to jumper the wires over to the power supply rails as shown
Traduit avec l'autorisation d'AdaFruit Industries - Translated with the permission from Adafruit Industries - www.adafruit.com
Toute référence, mention ou extrait de cette traduction doit être explicitement accompagné du texte suivant : « Traduction par MCHobby (www.MCHobby.be) - Vente de kit et composants » avec un lien vers la source (donc cette page) et ce quelque soit le média utilisé.
L'utilisation commercial de la traduction (texte) et/ou réalisation, même partielle, pourrait être soumis à redevance. Dans tous les cas de figures, vous devez également obtenir l'accord du(des) détenteur initial des droits. Celui de MC Hobby s'arrêtant au travail de traduction proprement dit.